LandPKS Learning
Habitat Hub
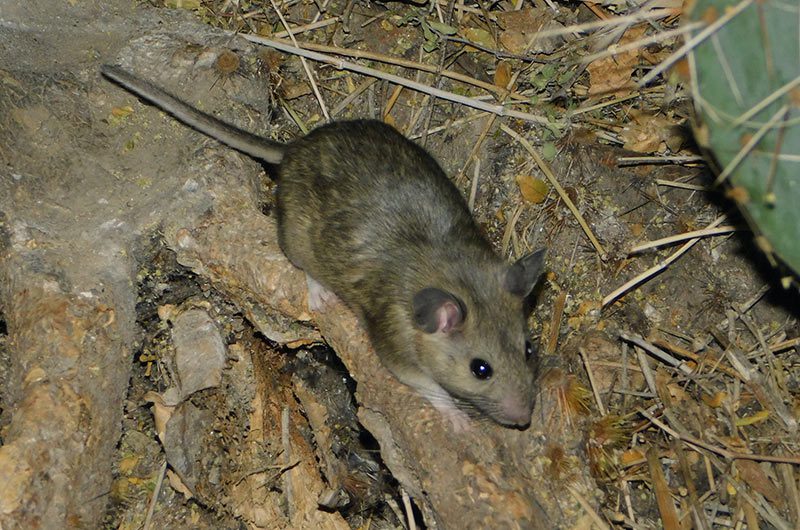

White-throated Woodrat
The white-throated woodrat is also called a packrat. They will live in burrows, caves, or construct elaborate middens of coarse woody debris, vegetation, and cactus joints. Middens or dens are built at the base of trees, shrubs, and cacti using locally available materials such as spiny plant parts from cholla, prickly pear, mesquite, and catclaw, likely as protection from predators. Middens can get as large as 3 ft/0.9 m high and 10 ft/3 m in diameter.
Neotoma albigula
Identification
The white-throated woodrat is a medium-sized rodent, generally with an 8 in/20 cm body, 5-7 in/13-17 cm tail, and weighing up to 1 lb/453 g. These rats have large ears and eyes and a relatively short, furry, not hairless, tail. The tail is grayish brown on the top and white on the underside. The woodrat’s body is gray or tawny with a white throat.
Observation Tips
White-throated woodrats are found in the United States Southwest (southern California, Utah, and Nevada, southwestern Colorado, western NM and all of Arizona) south into central Mexico. They are excellent climbers and may be found in shrubs and cacti above the ground. This solitary animal is active at night foraging and gathering materials for later use.
Interesting Fact
The white-throated woodrat is also called a packrat. They will live in burrows, caves, or construct elaborate middens of coarse woody debris, vegetation, and cactus joints. Middens or dens are built at the base of trees, shrubs, and cacti using locally available materials such as spiny plant parts from cholla, prickly pear, mesquite, and catclaw, likely as protection from predators. Cactus parts are preferred. These middens have several entrances and exits near the base with tunnels below ground, grass-lined sleeping areas, and areas for storage which can contain shiny objects from tin foil to keys. Middens can get as large as 3 ft/0.9 m high and 10 ft/3 m in diameter. Large middens are generally occupied by one adult or a female with her young.
Ideal Habitat
White-throated woodrats live in a variety of habitats, including desert, mixed, and conifer woodlands, including pinyon-juniper woodlands, ponderosa pine woodlands, and Madrean evergreen woodlands, bare rock and talus slopes, rocky cliffs, desert grasslands, and semiarid shrublands. They are most common in Sonoran and Chihuahuan desert grasslands and desert shrubland habitats. White-throated woodrats prefer eating cactus and other succulents where they also get much of their moisture. They also eat mesquite beans, yucca, catclaw, seeds, leaves, green vegetation, and fruits.
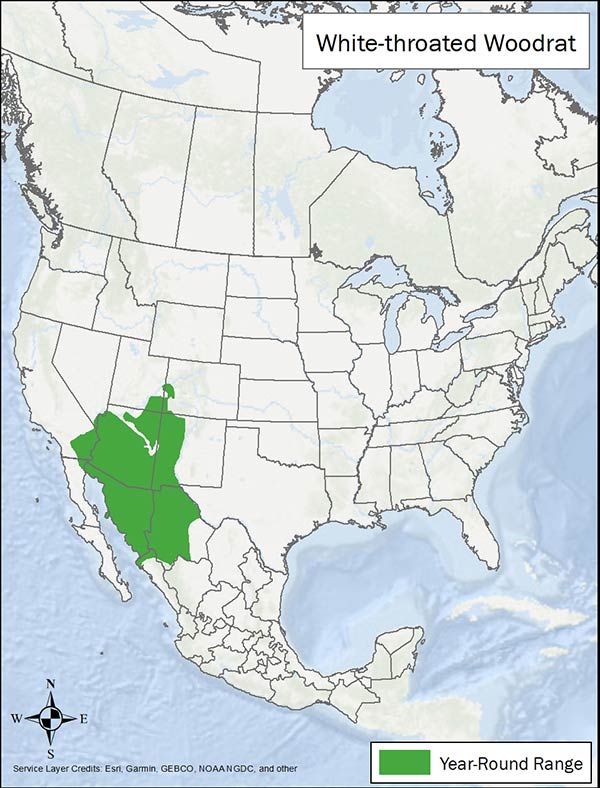
Range map provided by International Union for Conservation of Nature
Management Activities that Benefit Species – Best Management Practices (BMPs)
Maintain intact deserts, grasslands, shrublands, and woodlands. Retain a wide variety of cacti as woodrats consume many species to obtain food and water. Brush and cactus control should be carefully undertaken and not remove woody and succulent vegetation over large areas. Livestock grazing is compatible with white-throated woodrat habitat requirements as livestock generally avoid cacti or rarely significantly impact cacti densities.
Management Activities to Avoid
Avoid collecting cacti or allowing anyone to collect cacti off private lands. Avoid wide-spread brush or cactus control through using herbicide or mechanical treatments.
Other Species that Benefit from Similar Habitat Management
Management for white-throated woodrats including their predators – snakes, great horned owls, ringtails, bobcats, coyotes, and foxes.
Download
Download the White-throated Woodrat Factsheet
Other Resources
Arizona-Sonora Desert Museum. Factsheet White-throated Woodrat
California Department of Fish and Game. White-throated woodrat
International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). 2016. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2021-1. White-throated woodrat
NatureServe. 2021. NatureServe Explorer: An online encyclopedia of life [web application]. Version 7.1. NatureServe, Arlington, Virginia. Neotoma albigula
USFS. Fire Effects Information System. Neotoma albigula
Photo credit: Eric Hough/iNaturalist
Mobile App | Data Portal | Knowledge Hub | Habitat Hub | Learning Collections | Blog | About | Contact | Support



