LandPKS Learning
Habitat Hub
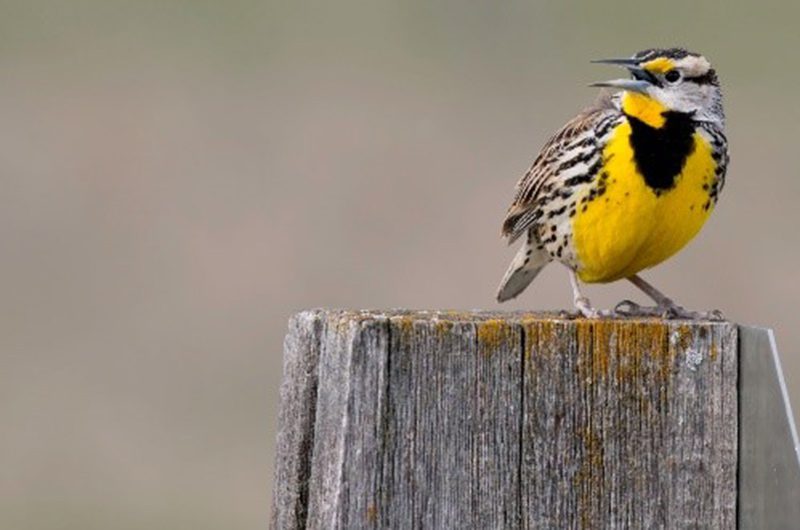

Eastern Meadowlark
There are up to 17 subspecies of eastern meadowlark including the isolated Lillian’s meadowlark, which is found in Arizona, New Mexico, and northern Mexico. Where eastern and western meadowlarks overlap in the Central Plains, they rarely hybridize or share territories. Although they look very similar, their songs sound completely different, and they will fight to defend their territories from one another.
Sturnella magna
Identification
Eastern meadowlarks are 8-10 in/21-26 cm long. They are chunky with a long, thin bill, short tail, and long legs. Males and females have brown streaky backs, a bright yellow chest with a black “V”, and white outer tail feathers. Females are less boldly marked than males. Eastern meadowlarks look very similar to western meadowlarks and are best distinguished by their different songs.
Observation Tips
In the spring and summer, eastern meadowlarks can be seen and heard singing their flute-like song from a tree, shrub, fencepost, or other perch. Birds may also sing a hurried, twittering song as they fly between perches. Eastern meadowlarks also give a variety of calls, like a sharp dzert for intruders and chatters and whistles when excited. They are mostly resident throughout their range in eastern North America and breed as far south as Central and northern South America. During the winter, they may feed in large flocks in fields looking for leftover seeds and grain.
Interesting Fact
There are up to 17 subspecies of eastern meadowlark including the isolated Lillian’s meadowlark, which is found in Arizona, New Mexico, and northern Mexico. Where eastern and western meadowlarks overlap in the Central Plains, they rarely hybridize or share territories. Although they look very similar, their songs sound completely different, and they will fight to defend their territories from one another.
Ideal Habitat
Eastern meadowlarks are associated with open country throughout their range. They are most commonly found in native grasslands, pastures, hayfields, agricultural fields, airports, along crop fields and roadsides, and in desert grassland and shrublands. Eastern meadowlarks can breed and establish territories in a variety of open habitats as small as 6 ac/0.4 ha. During nesting, they prefer areas with sufficient grass cover (>80%) and litter to conceal nests, which are placed on the ground, often in a shallow depression. Eastern meadowlarks tend to use wetter, lowlands where they overlap with western meadowlarks, and in the winter, they are often found in cultivated fields and feedlots.
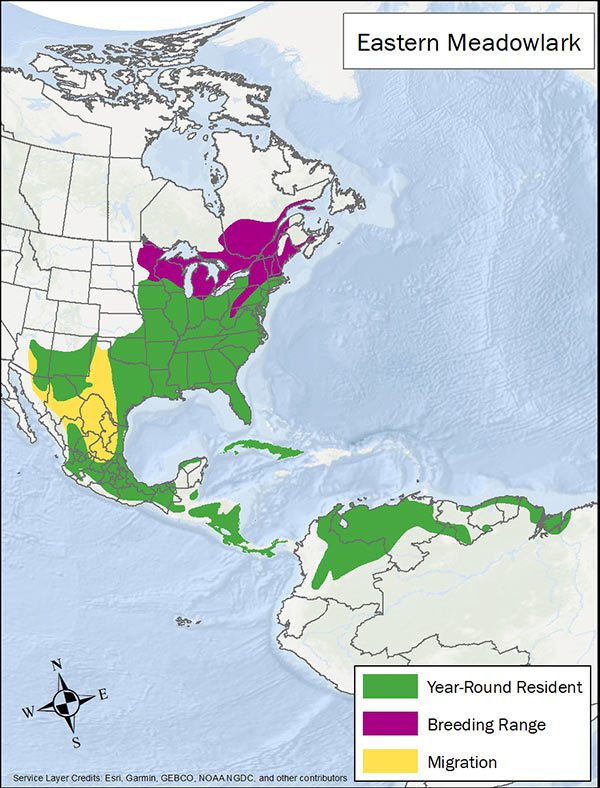
Range map provided by BirdLife International
Management Activities that Benefit Species – Best Management Practices (BMP’s)
Maintain high quality grassland habitat for eastern meadowlark breeding habitat. Also restore grassland habitat where appropriate in the United States by enrolling in the Conservation Reserve Program. Moderate grazing and rotational grazing both promote a diversity of grass height and density, which is beneficial for nesting and feeding meadowlarks. Mowing and haying may promote eastern meadowlark habitat, when delayed until August to reduce nest destruction. Mowing and haying every 3-5 years is best. Undercutting wheat stubble in the spring may prevent destruction of nests and young.
Management Activities to Avoid
Avoid burning grasslands every year, which reduces nesting habitat for eastern meadowlarks. Avoid conversion of grasslands to intensive agriculture. Avoid grazing grass heights to <4 in/10 cm. Avoid surface tillage in the spring for weed control, which can destroy nests and kill young. Avoid pesticide exposure as it can be harmful to adults and nestlings and reduce insect food sources.
Other Species that Benefit from Good Habitat Management
Other species that may benefit from habitat management for eastern meadowlarks include other species associated with open grasslands, such as grasshopper sparrows, dickcissels, and bobolinks.
Download
Dowload the Eastern Meadowlark factsheet
Descarga la ficha de los Pradero tortillaconchile
Other Resources
BirdLife International and Handbook of the Birds of the World. 2019. Bird species distribution maps of the world. Version 2019.1. Eastern Meadowlark
The Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Birds of the World Eastern Meadowlark
The Cornell Lab of Ornithology. All About Birds Eastern Meadowlark
Photo credit: Kelly Colgan Azar/Flickr
Mobile App | Data Portal | Knowledge Hub | Habitat Hub | Learning Collections | Blog | About | Contact | Support



