LandPKS Learning
Habitat Hub
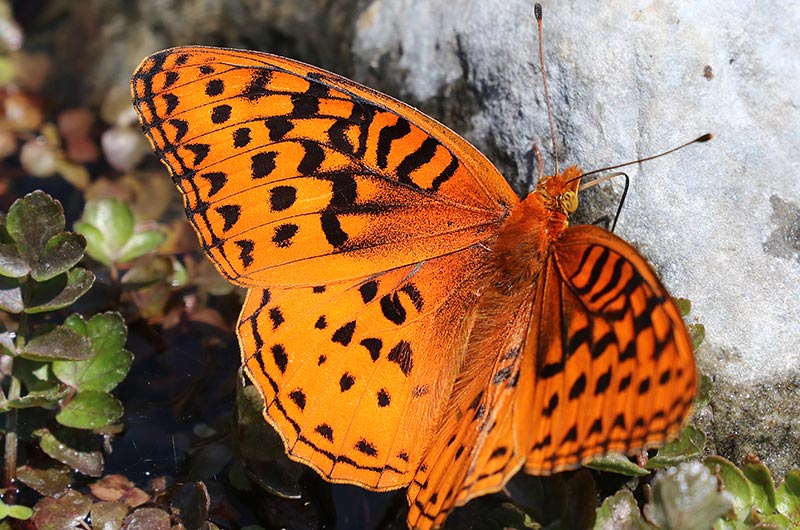

Nokomis Fritillary
A blue variant of Nokomis fritillary is found in northern Mexico.
Argynnis nokomis
Identification
Nokomis fritillary butterfly, also known as the Great Basin silverspot butterfly, has two sets of black or orange wings with dark colored veins. The male has a brownish orange upperside with dark patterns of dots and stripes along both wings. The female has black wings with cream-colored spots. Their wingspan can be 2.5 to 3 in/6-8 cm long. They both have darker undersides with cream-colored crescent shaped spots.
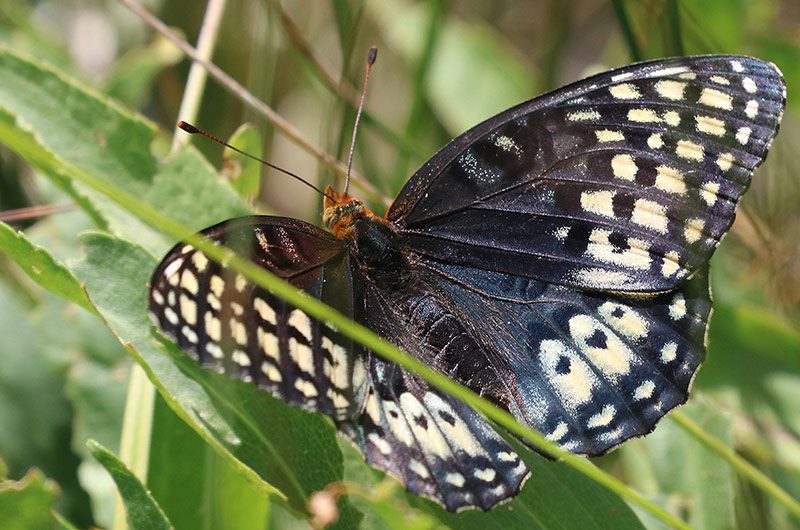

© Alan Schmierer / Flickr
Observation Tips
They range across the southwestern U.S. from California to Colorado and into Mexico. Males are easier to observe than females. Although Nokomis fritillary do not migrate, they are strong fliers. The Nokomis fritillary larval foodplant is bog violet, so look in moist meadows and other areas with nectar plants. During courtship, males are known to become active in early morning, scouting for females. Courtship flight and coupling has been observed midday in Arizona and New Mexico.
Interesting Fact
A blue variant of Nokomis fritillary is found in northern Mexico.
Ideal Habitat
The Nokomis fritillary feed on flower nectar, including that from thistles. They live in moist meadows, seeps, riparian areas, wetlands, and marshes with a variety of nectar plants. In the drier areas, wetlands are rare, therefore Nokomis fritillary populations are isolated. Nokomis fritillary are only found at sites with bog violets, the larval foodplant. Bog violets tend to grow in moist soil with plenty of shade.
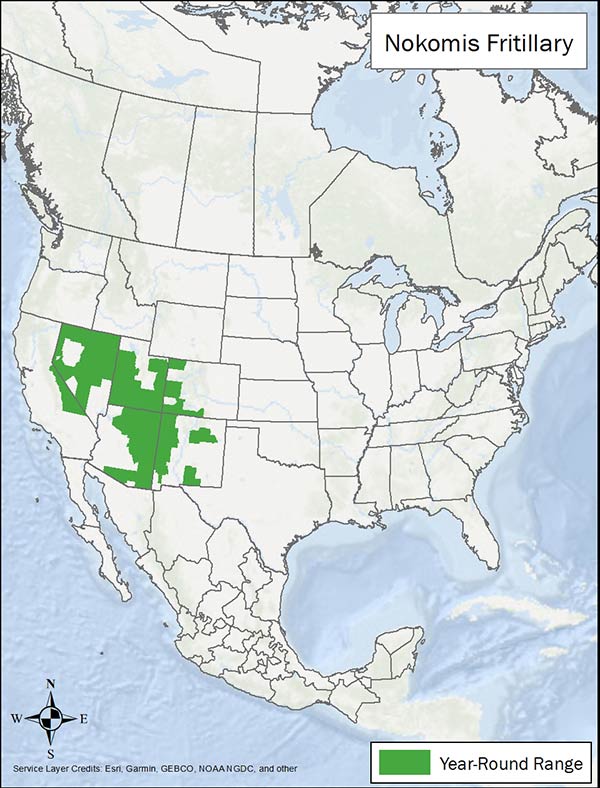
Range map provided by NatureServe and Butterflies and Months of North America (BAMONA). Note: Map only showing range in U.S.
Management Activities that Benefit Species – Best Management Practices (BMPs)
Restoring and maintaining bog violet is the most important conservation and management tool to provide habitat for Nokomis fritillary. Habitat management should also focus on ensuring nectar plants are diverse and abundant in areas near bog violets. Habitat areas such as riparian wetland communities with bog violet should be managed and maintained to provide habitat for the Nokomis fritillary.
Management Activities to Avoid
Avoid habitat loss of areas with bog violet and nectar plants through draining and degrading wetlands and riparian areas. Avoid heavy grazing (where the larval foodplant is damaged), and insecticide use in wetlands and riparian areas.
Other Species that Benefit from Similar Habitat Management
Management for Nokomis fritillary will benefit bog violets and nectar plants. The other animals who feed on those plants will also benefit, including other butterflies, and hummingbirds.
Download
Download the Nokomis Fritillary factsheet
Other Resources
Butterflies and Moths of North America. Nokomis Fritillary Speyeria. Data were provided by the Butterfly and Moth Information Network and the many participants who contribute to its Butterflies and Moths of North America project.
NatureServe. 2021. NatureServe Explorer: An online encyclopedia of life [web application]. Version 7.1. NatureServe, Arlington, Virginia. Argynnis Nokomis
USDA Forest Service. Great Basin Silverspot Butterfly
Mobile App | Data Portal | Knowledge Hub | Habitat Hub | Learning Collections | Blog | About | Contact | Support



